Science Fiction
Dictionary
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
The Far Side Of The Moon, By NASA (2015) And By PAUL (1932)

The first pictures of the lunar far side, were taken by the Soviet probe Luna 3 on October 7, 1959. In 2015, NASA took a series of pictures that were much more fun, showing the far side of the moon crossing over the full Earth:
A NASA camera aboard the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) satellite captured a unique view of the moon as it moved in front of the sunlit side of Earth last month. The series of test images shows the fully illuminated “dark side” of the moon that is never visible from Earth.The images were captured by NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC), a four megapixel CCD camera and telescope on the DSCOVR satellite orbiting 1 million miles from Earth. From its position between the sun and Earth, DSCOVR conducts its primary mission of real-time solar wind monitoring for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
EPIC maintains a constant view of the fully illuminated Earth as it rotates, providing scientific observations of ozone, vegetation, cloud height and aerosols in the atmosphere. Once EPIC begins regular observations next month, the camera will provide a series of Earth images allowing study of daily variations over the entire globe. About twice a year the camera will capture the moon and Earth together as the orbit of DSCOVR crosses the orbital plane of the moon.
These images were taken between 3:50 p.m. and 8:45 p.m. EDT on July 16, showing the moon moving over the Pacific Ocean near North America. The North Pole is in the upper left corner of the image. It is in the original orientation as taken by the spacecraft.
(Via NASA.)
Who could even visualize such a picture? As it turns out, science fiction illustrator Frank R. Paul drew this illustration for "The Voyage of the Asteroid", a story by Laurence Manning, published in Wonder Stories Quarterly in 1932.
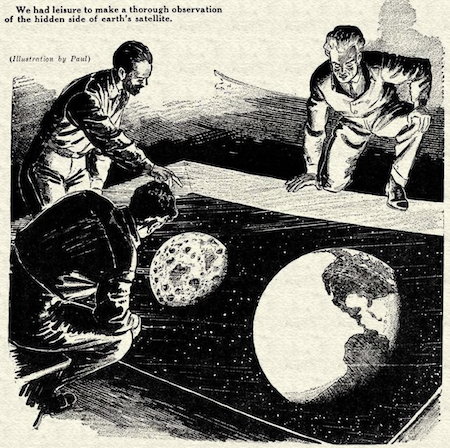

(The hidden side of earth's satellite)
Paul's picture shows a slightly different orientation, one in which the earth and the moon are not pictured at "full", but rather "gibbous", which I think makes for a more three-dimensional representation.
Update 15-Dec-2022:
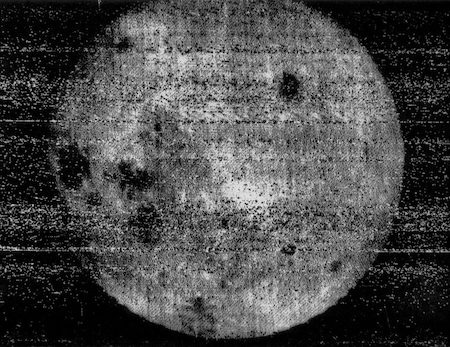
(First photograph of lunar farside taken in 1959)
This photograph was taken by the Soviet spacecraft Luna 3, which was launched a month after the Luna 2 spacecraft became the first man-made object to impact on the surface of the Moon,” explains astronomer Kevin Hainline in a recent Twitter thread. “Luna 2 followed Luna 1, the first spacecraft to escape a geosynchronous Earth orbit.” Luna 3 was designed to take photographs of the Moon.
End update.
Scroll down for more stories in the same category. (Story submitted 9/19/2022)
Follow this kind of news @Technovelgy.| Email | RSS | Blog It | Stumble | del.icio.us | Digg | Reddit |
Would
you like to contribute a story tip?
It's easy:
Get the URL of the story, and the related sf author, and add
it here.
Comment/Join discussion ( 0 )
Related News Stories - (" Space Tech ")
The New Habitable Zones Include Asimov's Ribbon Worlds
'...there's a narrow belt where the climate is moderate.' - Harl Vincent, 1931.
Will Space Stations Have Large Interior Spaces Again?
'They filed clumsily into the battleroom, like children in a swimming pool for the first time, clinging to the handholds along the side.' - Orson Scott Card, 1985.
Reflect Orbital Offers 'Sunlight on Demand' And Light Pollution
'I don't have to tell you about the seven two-mile-diameter orbital mirrors...'
Chrysalis Generation Ship to Alpha Centauri
'This was their world, their planet —
this swift-traveling, yet seemingly moveless vessel.' - Nat Schachner, 1934
Technovelgy (that's tech-novel-gee!) is devoted to the creative science inventions and ideas of sf authors. Look for the Invention Category that interests you, the Glossary, the Invention Timeline, or see what's New.
Science Fiction
Timeline
1600-1899
1900-1939
1940's 1950's
1960's 1970's
1980's 1990's
2000's 2010's
Current News
The New Habitable Zones Include Asimov's Ribbon Worlds
'...there's a narrow belt where the climate is moderate.'
Can One Robot Do Many Tasks?
'... with the Master-operator all you have to do is push one! A remarkable achievement!'
Atlas Robot Makes Uncomfortable Movements
'Not like me. A T-1000, advanced prototype. A mimetic poly-alloy. Liquid metal.'
Boring Company Drills Asimov's Single Vehicle Tunnels
'It was riddled with holes that were the mouths of tunnels.'
Humanoid Robots Tickle The Ivories
'The massive feet working the pedals, arms and hands flashing and glinting...'
A Remarkable Coincidence
'There is a philosophical problem of some difficulty here...'
Cortex 1 - Today A Warehouse, Tomorrow A Calculator Planet
'There were cubic miles of it, and it glistened like a silvery Christmas tree...'
Perching Ambush Drones
'On the chest of drawers something was perched.'
Leader-Follower Autonomous Vehicle Technology
'Jason had been guiding the caravan of cars as usual...'
Golf Ball Test Robot Wears Them Out
"The robot solemnly hit a ball against the wall, picked it up and teed it, hit it again, over and again...'
Boring Company Vegas Loop Like Asimov Said
'There was a wall ahead... It was riddled with holes that were the mouths of tunnels.'
Rigid Metallic Clothing From Science Fiction To You
'...support the interior human structure against Jupiter’s pull.'
Is The Seattle Ultrasonics C-200 A Heinlein Vibroblade?
'It ain't a vibroblade. It's steel. Messy.'
Roborock Saros Z70 Is A Robot Vacuum With An Arm
'Anything larger than a BB shot it picked up and placed in a tray...'
A Beautiful Visualization Of Compact Food
'The German chemists have discovered how to supply the needed elements in compact, undiluted form...'
Bone-Building Drug Evenity Approved
'Compounds devised by the biochemists for the rapid building of bone...'
